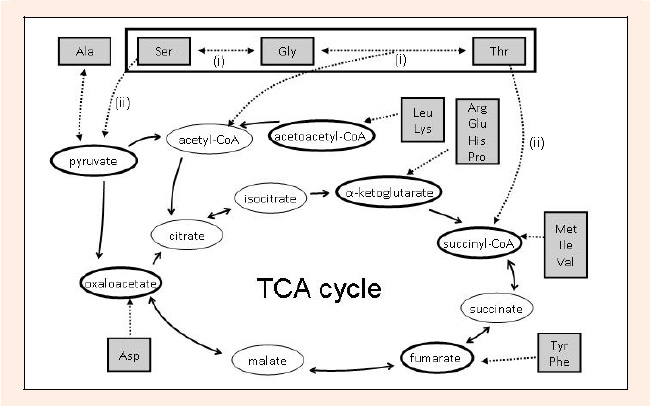
Scheme. Amino acid catabolism in the gluconeogenesis pathway in rat. Serine, glycine, and threonine are reversibly and enzymatically interconverted via serine hydroxymethyltransferase (i). Serine is catabolized to pyruvate through a deamination reaction by serine/threonine dehydratase (ii). Threonine is also converted to acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA via these enzymes. The amino acids are categorized by the respective compounds in gluconeogenesis/ketogenesis to which they are precursors: Ser, Gly, Thr, and Ala; pyruvate, Leu and Lys; acetoacetyl-CoA, Arg, Glu, His, and Pro; -ketoglutarate, Met, Ile, and Val; succinyl-CoA, Tyr and Phe; fumarate, Asp; oxaloacetate precursors.